Hooke’s
Law – Computer Applications Assignment 1
Hooke’s Law is the law of elasticity discovered by Robert Hooke in 1660, which
states that, for relatively small deformations of an object, the displacement
or size of the deformation is directly proportional to the deforming force or load.
(1)
Deformation of a solid is caused by a force that can either
be compressive or tensile when applied in one direction. Compressive forces try to compress and object
while tensile ones try to tear it apart. We can study these effects by looking
at what happens when you compress or extend a spring. (2)
The equation which relates deformation to load is written
as;
F=-kx (Equation 1(3))
In equation 1, F is equal to the force applied; k is the
spring constant of the material and x is the amount of displacement observed.
When plotting a graph of load against displacement, a linear
relationship is observed.
(Figure 1 (2))

(Figure 2 (2))
(Figure 3 (2))
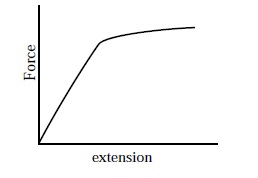
Figure 2 shows the relationship between force and extension
for a strong, brittle material. There is very little extension for a large
force, but the material suddenly breaks and fractures. It is defined as being
brittle because the material fractures instead of bending. An example of a brittle material is glass. (2)
Figure 3 shows the relationship between force and extension
for a plastic material. The material undergoes a large deformation with only a
little force applied. The linear relationship of Hooke’s Law only lasts for a
short time. It is defined as being plastic because it is more likely to bend
than to fracture. (2)
(Figure 4 (2))
Figure 4 shows the relationship between force and extension
for a ductile material. The material shows the behaviour of a plastic material,
after Hooke’s Law has been exceeded, over a range of forces before
fracturing. Ductility is the ability of
a material to be stretched into a new shape without breaking. An example of a ductile material is aluminium. (2)
Most Hooke’s Law experiments are carried out by hanging
weights onto a spring and recording how much they extend by. Here is a video demonstrating how to set up and conduct a Hooke's Law experiment.
Figure 5 shows how when the force acting on the spring doubles, the spring's extension also doubles.
(Figure 5 (5))
Here are a few videos
which explain Hooke’s Law and what to expect from a force and displacement
graph.
The following results were obtained from a Hooke’s Law
experiment.
x
|
y1
(Material 1)
|
y2
(Material 2)
|
z
(Material 3)
|
1
|
3
|
2.2583
|
2.375
|
2
|
4.5
|
4.3166
|
9.375
|
3
|
6
|
6.3749
|
28.375
|
4
|
7.5
|
8.4332
|
65.375
|
5
|
9
|
10.4915
|
126.375
|
6
|
10.5
|
12.5498
|
217.375
|
7
|
13
|
14.6081
|
344.375
|
8
|
14
|
16.6664
|
513.375
|
9
|
15
|
18.7247
|
730.375
|
(Table 1)
In table 1, x is the amount of force applied in Newtons, and
the values shown in the material columns show the amount of deformation in the
material in mm. When plotting materials
1 and 2 on a graph, a trend becomes evident.
(Figure 6)
Figure 6 shows, that both materials have a linear
relationship with force and extension. This means that Hooke’s law is being
obeyed throughout all points of the experiment. This also implies that, once
the load is removed, the material will return to its original shape. Also, as
the relationship is linear, they both follow equation 4 which is the equation
of a straight line.
Y=mx+c (Equation 4)
Using equation 4, it is possible to work out the gradient of
the slope and also the y intercept. In equation 4, the gradient of the slope is
equal to m and the y intercept is equal to c. In this case, the gradient is a
constant and is also equal to the spring constant of the material itself. Equation
2 shows the spring constant for material 1 as being 1.5583 Nm-1.
Equation 3 shows that the spring constant for material 2 as being 2.0583 Nm-1.
The y intercept shows the force applied when displacement is
zero. It is to be expected that the y intercept for Hooke’s law will be equal
to zero. That is to say, that when there is zero force applied, zero
deformation is observed. However, as can be seen from equations 2 and 3, there
is a value of 0.2 and 1.375 respectively. These values obtained for the y
intercept is due to choosing a line of best fit from the data collected.
It is also possible to use the graph in figure 6 to show the
point where the force-extension relationships for both materials intersect each
other. It is at this point where both materials will extend by the same amount
when the same force is applied to them. According to the graph this occurs at
roughly 2.3N. This can also be attained by using the laws of simultaneous
equations to equations 2 and 3 in the following way.
First arrange the equations together as equation 2 is equal
to equation 3 to get equation 5;
2.0583x + 0.2 =
1.5583x + 1.375 (Equation 5)
Next, make x the subject of equation 5 to get equation 6;
2.0583x – 1.5583x
= 1.375 – 0.2 (Equation 6)
Next, do the subtraction on both sides of the equation to get
equation 7;
0.5x = 1.175 (Equation
7)
Finally divide both sides of equation 7 by 0.5 to leave
equation 8;
X = 2.35 N (Equation
8)
The value which appears on figure 6 is very close to the
value obtained in equation 8. It is not identical due to the graph in figure 6
not being presented in enough detail to gain an exact reading of where the
intersection takes place.
(Figure 7)
References
1.
Unknown. (2012). Hooke's Law. Available:
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/271336/Hookes-law. Last accessed 12th
Nov 2012.
2.
Unknown. (6th Oct 2009). What Is Hooke's Law?. Available:
http://engineers4world.blogspot.co.uk/2009/11/hookes-law.html. Last accessed
12th Nov 2012.
3.
Unknown. (2012). Determine The Spring Constant. Available:
http://www.4physics.com/phy_demo/HookesLaw/HookesLawLab.html. Last accessed
12th Nov 2012.
4.
QuantumBoffin. (7th Nov 2009). Stretching a Spring. Available:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OHyfoM2vIUs&feature=related. Last accessed
13th Nov 2012.
5.
Nave, R. (Unknown). Elasticity
- Hooke's Law. Available:
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/permot2.html. Last accessed 13th Nov
2012.
6.
Fullerton, D. (29th Nov 2011). Springs
and Hookes Law. Available:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6MhaPzGxfV8&feature=related. Last
accessed 13th Nov 2012.





ok thank u for the information on Hookes law and springs I am really able to explain coz I have understood the concept
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing such a nice piece of information with us.White command hooks
ReplyDeleteThanks for every other excellent post. The place else may just anyone get that kind of info in such an ideal manner of writing? I’ve a presentation subsequent week, and I am at the look for such information. محامي
ReplyDeleteGreat post. I am a regular visitor of your web site and appreciate you taking the time to maintain the nice site. I will be a frequent visitor for a really long time. اسال محامي على الإنترنت
ReplyDeleteيأتي الاختيار الجيد والناجح دائمًا من العلم والمعرفة والوعي والإدراك. ربما كانت لدينا خيارات خلال حياتنا فشلت دون معرفة ، والزواج مثال واضح ، ولكن المعرفة والوعي لاختيار محامي في جدة ، ما هي الطرق الممكنة؟
ReplyDelete8 خصائص مهمة للمحامين الخبراء ، أين يمكننا أن نجد أخيرًا محاميًا جيدًا؟
اليوم ، مع الوضع الاقتصادي الحالي ، الذي ليس على مرمى حجر ، نواجه جميعًا مشاكل ومشاكل قانونية ، ووجود محامٍ جيد ومتخصص أكثر ضرورة من أي حاجة أخرى.
على الرغم من أنه من السهل جدًا ان تستخدم خدمة ابحث عن محامي ، إلا أنه من الصعب بالتأكيد معرفة محامٍ جيد وذوي خبرة ، وهو ما أصبح ممكنًا بفضل نظام Top Lawyer .
بعبارة أخرى ، فإن نظام المحامي ، باعتباره أحدث نظام قانوني عبر الإنترنت ، من خلال توفير السير الذاتية العلمية والعملية لجميع المحامين في جميع أنحاء إيران ، قد أتاح لك الوصول بسهولة إلى المحامي الذي تريده في أي تخصص ، في أقصر وقت ممكن. ابحث وكن قادرًا على الحصول على استشارة مجانية وتقييم.
لماذا يجب أن يكون لدينا محامي في الرياض ؟
كما هو الحال عندما نمرض ، إذا لم نذهب إلى الطبيب ونحاول العلاج الذاتي ، بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، لن يختفي المرض ، وحتى مع مرور الوقت ، قد تعرضنا مضاعفات العلاج الذاتي لخطر الموت. القضايا القانونية ، مثل القضايا الطبية ، معقدة للغاية إذا تمت بدون استشارة ودون الاستعانة بمحامين ذوي خبرة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، لن يتم حل المشكلة ، بل ستؤدي إلى خسائر مالية أو بشرية فادحة مع عواقب لا يمكن إصلاحها.
اختصاصات محامي بالرياض
من هو افضل محامي في الرياض بالمملكة العربية السعودية ؟
ReplyDeleteمحامي في الرياض ، هو مكتب افضل محامي في الرياض وسائر مناطق ومدن المملكة العربية السعودية،يضم المكتب العربي للقانون طاقم متخصص من افضل المحامين في الرياض
محامي بالرياض من هو افضل محامي في الرياض وما هو رقمه ؟ السؤال الذي يطرحه الكثير منا على بعضنا البعض عند التعامل مع المشكلات القانونية .
حقاً أين أجد افضل محامي بالرياض مناسب لجميع القضايا القانونية بما في ذلك القضايا التجارية والطلاق والاحوال الشخصية ونقل الملكيات والشيكات والمحاكم العمالية ؟
اذا كنت تبحث أيضاً عن افضل محامي في جدة فيسعدنا إخبارك باننا نضم افضل محامي بجدة خبرة وعلماً على مستوى المملكة العربية السعودية.